5. Lenguajes de bases de datos
5.1 Introducción
Los lenguajes de consulta (query language) son especificaciones formales para representar consultas. Aún cuando son llamados de "consulta" en realidad pueden hacer mucho más que consultas.
5.2 Structured Query Language (SQL)
- Creado por IBM alrededor de los años 70s
- Combinación de álgebra relacional y cálculo relacional
- En 1986 ANSI e ISO lo estandarizan en SQL-86
- Otras versiones: SQL-92, SQL-99
- Más info: http://www.wiscorp.com/SQLStandards.html
5.2.1 Data Manipulation Language (DML)
INSERT
insert into table_name (column_name, ..., column_name) |
insert into musicians (musician_id, last_name, first_name, nickname) |
| insert into musicians values (2,'Lydon','John','Johnny Rotten'); |
INSERT [LOW_PRIORITY | DELAYED] [IGNORE]
[INTO] tbl_name [(col_name,...)]
VALUES ((expression | DEFAULT),...),(...),...
[ ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE col_name=expression, ... ]
or INSERT [LOW_PRIORITY | DELAYED] [IGNORE]
[INTO] tbl_name [(col_name,...)]
SELECT ...
or INSERT [LOW_PRIORITY | DELAYED] [IGNORE]
[INTO] tbl_name
SET col_name=(expression | DEFAULT), ...
[ ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE col_name=expression, ... ]
|
UPDATE
update table_name |
update albums |
update albums |
UPDATE [LOW_PRIORITY] [IGNORE] tbl_name
SET col_name1=expr1 [, col_name2=expr2 ...]
[WHERE where_definition]
[ORDER BY ...]
[LIMIT row_count]
or: UPDATE [LOW_PRIORITY] [IGNORE] tbl_name [, tbl_name ...]
SET col_name1=expr1 [, col_name2=expr2 ...]
[WHERE where_definition] |
DELETE
delete from table_name |
delete from albums |
DELETE [LOW_PRIORITY] [QUICK] [IGNORE] FROM table_name
[WHERE where_definition]
[ORDER BY ...]
[LIMIT row_count]
or: DELETE [LOW_PRIORITY] [QUICK] [IGNORE]
table_name[.*] [, table_name[.*] ...]
FROM table-references
[WHERE where_definition]
or: DELETE [LOW_PRIORITY] [QUICK] [IGNORE]
FROM table_name[.*] [, table_name[.*] ...]
USING table-references
[WHERE where_definition]
|
SELECT
select column_name, ..., column_name |
select title |
SELECT [STRAIGHT_JOIN]
[SQL_SMALL_RESULT] [SQL_BIG_RESULT] [SQL_BUFFER_RESULT]
[SQL_CACHE | SQL_NO_CACHE] [SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS] [HIGH_PRIORITY]
[DISTINCT | DISTINCTROW | ALL]
select_expression,...
[INTO {OUTFILE | DUMPFILE} 'file_name' export_options]
[FROM table_references
[WHERE where_definition]
[GROUP BY {unsigned_integer | col_name | formula}
[ASC | DESC], ... [WITH ROLLUP]]
[HAVING where_definition]
[ORDER BY {unsigned_integer | col_name | formula}
[ASC | DESC] ,...]
[LIMIT [offset,] row_count | row_count OFFSET offset]
[PROCEDURE procedure_name(argument_list)]
[FOR UPDATE | LOCK IN SHARE MODE]]
table_name [[AS] alias]
[[USE INDEX (key_list)]
| [IGNORE INDEX (key_list)]
| [FORCE INDEX (key_list)]]
|
JOIN
select bands.band_name |
| SELECT t1.name, t2.salary FROM employee AS t1, info AS t2 -> WHERE t1.name = t2.name; |
| SELECT table1.* FROM table1 -> LEFT JOIN table2 ON table1.id=table2.id -> WHERE table2.id IS NULL; |
table_reference, table_reference
table_reference [INNER | CROSS] JOIN table_reference [join_condition]
table_reference STRAIGHT_JOIN table_reference
table_reference LEFT [OUTER] JOIN table_reference [join_condition]
table_reference NATURAL [LEFT [OUTER]] JOIN table_reference
{ OJ table_reference LEFT OUTER JOIN table_reference
ON conditional_expr }
table_reference RIGHT [OUTER] JOIN table_reference [join_condition]
table_reference NATURAL [RIGHT [OUTER]] JOIN table_reference |
UNION
| (SELECT a FROM table_name WHERE a=10 AND B=1 ORDER BY a LIMIT 10) UNION (SELECT a FROM table_name WHERE a=11 AND B=2 ORDER BY a LIMIT 10) ORDER BY a; |
SELECT ... UNION [ALL | DISTINCT] SELECT ... [UNION [ALL | DISTINCT] SELECT ...] |
SUBQUERIES
select title |
INDEX
| CREATE INDEX part_of_name ON customer (name(10)); |
| CREATE INDEX two_attributes ON customer (name(10), balance); |
CREATE [UNIQUE|FULLTEXT] INDEX index_name [index_type]
ON tbl_name (index_col_name,...)
index_col_name:
col_name [(length)] [ASC | DESC] |
SHOW INDEX FROM tbl_name DROP INDEX index_name ON tbl_name |
EXPLAIN
explain table_name;
explain select...;
|
5.2.2 Data Definition Language (DDL)
CREATE
create table table_name ( |
create table musicians( |
CREATE [TEMPORARY] TABLE [IF NOT EXISTS] tbl_name [(create_definition,...)]
[table_options] [select_statement]
or: CREATE [TEMPORARY] TABLE [IF NOT EXISTS] tbl_name [(] LIKE old_tbl_name [)];
create_definition:
col_name type [NOT NULL | NULL] [DEFAULT default_value] [AUTO_INCREMENT]
[[PRIMARY] KEY] [COMMENT 'string'] [reference_definition]
| [CONSTRAINT [symbol]] PRIMARY KEY [index_type] (index_col_name,...)
| KEY [index_name] [index_type] (index_col_name,...)
| INDEX [index_name] [index_type] (index_col_name,...)
| [CONSTRAINT [symbol]] UNIQUE [INDEX] [index_name] [index_type] (index_col_name,...)
| FULLTEXT [INDEX] [index_name] (index_col_name,...)
| [CONSTRAINT [symbol]] FOREIGN KEY [index_name] (index_col_name,...)
[reference_definition]
| CHECK (expr)
type:
TINYINT[(length)] [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL]
| SMALLINT[(length)] [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL]
| MEDIUMINT[(length)] [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL]
| INT[(length)] [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL]
| INTEGER[(length)] [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL]
| BIGINT[(length)] [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL]
| REAL[(length,decimals)] [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL]
| DOUBLE[(length,decimals)] [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL]
| FLOAT[(length,decimals)] [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL]
| DECIMAL(length,decimals) [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL]
| NUMERIC(length,decimals) [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL]
| CHAR(length) [BINARY | ASCII | UNICODE]
| VARCHAR(length) [BINARY]
| DATE
| TIME
| TIMESTAMP
| DATETIME
| TINYBLOB
| BLOB
| MEDIUMBLOB
| LONGBLOB
| TINYTEXT
| TEXT
| MEDIUMTEXT
| LONGTEXT
| ENUM(value1,value2,value3,...)
| SET(value1,value2,value3,...)
index_col_name:
col_name [(length)] [ASC | DESC]
reference_definition:
REFERENCES tbl_name [(index_col_name,...)]
[MATCH FULL | MATCH PARTIAL]
[ON DELETE reference_option]
[ON UPDATE reference_option]
reference_option:
RESTRICT | CASCADE | SET NULL | NO ACTION | SET DEFAULT
table_options: table_option [table_option] ...
table_option:
{ENGINE | TYPE} = {BDB | HEAP | ISAM | InnoDB | MERGE | MRG_MYISAM | MYISAM}
| AUTO_INCREMENT = #
| AVG_ROW_LENGTH = #
| CHECKSUM = {0 | 1}
| COMMENT = 'string'
| MAX_ROWS = #
| MIN_ROWS = #
| PACK_KEYS = {0 | 1 | DEFAULT}
| PASSWORD = 'string'
| DELAY_KEY_WRITE = {0 | 1}
| ROW_FORMAT = { DEFAULT | DYNAMIC | FIXED | COMPRESSED }
| RAID_TYPE = { 1 | STRIPED | RAID0 } RAID_CHUNKS=# RAID_CHUNKSIZE=#
| UNION = (table_name,[table_name...])
| INSERT_METHOD = { NO | FIRST | LAST }
| DATA DIRECTORY = 'absolute path to directory'
| INDEX DIRECTORY = 'absolute path to directory'
| DEFAULT CHARACTER SET character_set_name [COLLATE collation_name]
select_statement:
[IGNORE | REPLACE] [AS] SELECT ... (Some legal select statement) |
FOREIGN CONSTRAINTS
[CONSTRAINT symbol] FOREIGN KEY [id] (index_col_name, ...)
REFERENCES tbl_name (index_col_name, ...)
[ON DELETE {CASCADE | SET NULL | NO ACTION | RESTRICT}]
[ON UPDATE {CASCADE | SET NULL | NO ACTION | RESTRICT}]
|
CREATE TABLE parent(id INT NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (id) ) |
CREATE TABLE product (category INT NOT NULL, id INT NOT NULL, price DECIMAL, PRIMARY KEY(category, id)) ENGINE=INNODB; |
DROP
DROP [TEMPORARY] TABLE [IF EXISTS] tbl_name [, tbl_name,...] [RESTRICT | CASCADE] |
ALTER
ALTER TABLE t1 MODIFY b BIGINT NOT NULL; |
ALTER [IGNORE] TABLE tbl_name alter_specification [, alter_specification] ...
alter_specification:
ADD [COLUMN] create_definition [FIRST | AFTER column_name ]
| ADD [COLUMN] (create_definition, create_definition,...)
| ADD INDEX [index_name] [index_type] (index_col_name,...)
| ADD [CONSTRAINT [symbol]] PRIMARY KEY [index_type] (index_col_name,...)
| ADD [CONSTRAINT [symbol]] UNIQUE [index_name] [index_type] (index_col_name,...)
| ADD FULLTEXT [index_name] (index_col_name,...)
| ADD [CONSTRAINT [symbol]] FOREIGN KEY [index_name] (index_col_name,...)
[reference_definition]
| ALTER [COLUMN] col_name {SET DEFAULT literal | DROP DEFAULT}
| CHANGE [COLUMN] old_col_name create_definition
[FIRST | AFTER column_name]
| MODIFY [COLUMN] create_definition [FIRST | AFTER column_name]
| DROP [COLUMN] col_name
| DROP PRIMARY KEY
| DROP INDEX index_name
| DISABLE KEYS
| ENABLE KEYS
| RENAME [TO] new_tbl_name
| ORDER BY col
| CHARACTER SET character_set_name [COLLATE collation_name]
| table_options
|
DATABASE
CREATE DATABASE [IF NOT EXISTS] db_name
[create_specification [, create_specification] ...]
create_specification:
[DEFAULT] CHARACTER SET charset_name
| [DEFAULT] COLLATE collation_name |
DROP DATABASE db_name |
GRANTS
GRANT priv_type [(column_list)] [, priv_type [(column_list)] ...]
ON {tbl_name | * | *.* | db_name.*}
TO user_name [IDENTIFIED BY [PASSWORD] 'password']
[, user_name [IDENTIFIED BY [PASSWORD] 'password'] ...]
[REQUIRE
NONE |
[{SSL| X509}]
[CIPHER cipher [AND]]
[ISSUER issuer [AND]]
[SUBJECT subject]]
[WITH [GRANT OPTION | MAX_QUERIES_PER_HOUR # |
MAX_UPDATES_PER_HOUR # |
MAX_CONNECTIONS_PER_HOUR #]]
REVOKE priv_type [(column_list)] [, priv_type [(column_list)] ...]
ON {tbl_name | * | *.* | db_name.*}
FROM user_name [, user_name ...]
REVOKE ALL PRIVILEGES,GRANT OPTION FROM user_name [, user_name ...]
Ejemplos en Mysql
MySQL has four privilege levels: |
VIEWS
CREATE [ OR REPLACE ] VIEW name [ ( column_name [, ...] ) ] AS query |
CREATE VIEW comedies AS
SELECT * FROM films WHERE kind = 'Comedy'; |
TRIGGERS
CREATE
DROP TRIGGER [schema_name.]trigger_name
|
mysql> CREATE TABLE account (acct_num INT, amount DECIMAL(10,2)); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec) mysql> CREATE TRIGGER ins_sum BEFORE INSERT ON account -> FOR EACH ROW SET @sum = @sum + NEW.amount; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.06 sec) |
5.3 QUEL
5.3.1 Antecedentes
- Desarrollado por M. Stonebraker en 1976
- Lenguaje original de "ingres"
- Basado en el cálculo relacional de tuplas
5.3.2 Componentes
- Declaración de variables tuplas
range of t is r
- recuperación de tuplas
retrieve (ti.aj... )
- filtrado
where P
- no se permiten queries anidados
- no provee unión, intersección ni resta.
5.3.2.1 Ejemplos básicos
nombres de estudiantes de ing. en sistemas
range of e is estudiantes
retrieve unique (e.nombre)
where e.carrera='is'datos de estudiantes de ing. en sistemas
range of e is estudiantes
retrieve (e.all)
where e.carrera='is'nombres de estudiantes que han reprobado
range of e is estudiantes
range of c is est_cursos
retrieve unique (e.nombre)
where e.id=c.id and c.calif < 7.5
5.3.3 Funciones agregadas: count,sum, max, avg, min
formato
agregado(t.a)
agregado(t.a where P)
agregado(t.a by s.b1, s.b2,..s.bn where P)
5.3.3.1 Ejemplos
Promedio de calificaciones del depto de is
range of t is est_cursos
retrieve avg(t.calif where depto='is')id de estudiantes con alguna calificacion mayor al promedio
range of e is est_cursos
range of s is est_cursos
retrieve unique(e.id)
where e.calif > avg(s.calif)
5.3.4 Quel tambien posee la manera de agregar, actualizar y eliminar tuplas.
eliminar los estudiantes de is con id menor a 123456
range of t is estudiantes
delete t
where t.id < 123456
5.4 Query by example QBE
5.4.1 Antecedentes
- Desarrollo de ibm en los 70s
- Ejemplo de programación visual
- Sintáxis bidimensional
- Genera consultas a partir de ejemplos
- Relación directa con cálculo relacional de tuplas
5.4.2 Estructura
- plantillas de tablas con renglones
- variables de dominio (_x, _y, etc)
- comandos, palabras clave (P., ALL.,...)
5.4.3 Ejemplos
a) id y nombre de los estudiantes de ingenieria en sistemas
| estudiantes | id | nombre | carrera |
| P._x | P._y | is |
b) todos los datos de todos los estudiantes
| estudiantes | id | nombre | carrera |
| P._x | P._y | P._z |
o bien
| estudiantes | id | nombre | carrera |
| P. |
c) nombres de los estudiantes de is incluyendo duplicados
| estudiantes | id | nombre | carrera |
| P.ALL. | is |
d) ids de estudiantes que han tomado los cursis is 441 y is 323
| est_cursos | id | depto | num | calif |
| P._x | is | 441 | ||
| _x | is | 323 |
e) nombres de estudiantes de ing en sistemas que han reprobado algun curso
| estudiantes | id | nombre | carrera |
| _x | P.ALL. | is |
| est_cursos | id | depto | num | calif |
| _x | < 7.5 |
f) ids de estudiantes que han tomado cursos con el estudiante 777
| est_cursos | id | depto | num | calif |
| 777 | _y | _z | ||
| P._x | _y | _z |
g) nombres de estudiantes que no son empleados
| estudiantes | id | nombre | carrera |
| _x | P.ALL. |
| est_empl | id | nombre | area | carrera |
| ¬ | _x |
promedio de calificaciones del estudiante 777 en cursos que no son de is
| est_cursos | id | depto | num | calif |
| 777 | ¬ is | P.AVG.ALL. |
5.4.4 QBE en Microsoft Access
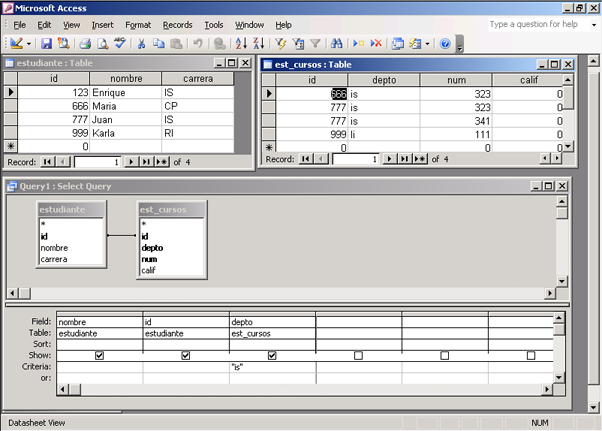 |